如果只是定义一个 slice 或者 map 的变量,而不进行初始化,那么任何操作都会引起中断错误,当没有显式初始化的时候必须使用make函数初始化,根据需要合理的指定元素参数有助于性能提升.
slice 引用类型。主要数据结构是数组,但是本身本定义为结构体,值拷贝传递。
len表示可用元素数量,读写操作不能超过该限制。cap表示最大容量,不超过底层数组长度。- 如果值为
nil,cap和len的结果都是0。
slice结构示意:
1
2
|
data := [...]int{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
slice := data[1:4:5] // [low : high : max]
|
-
len = high - low //3
-
cap = max - low // 4
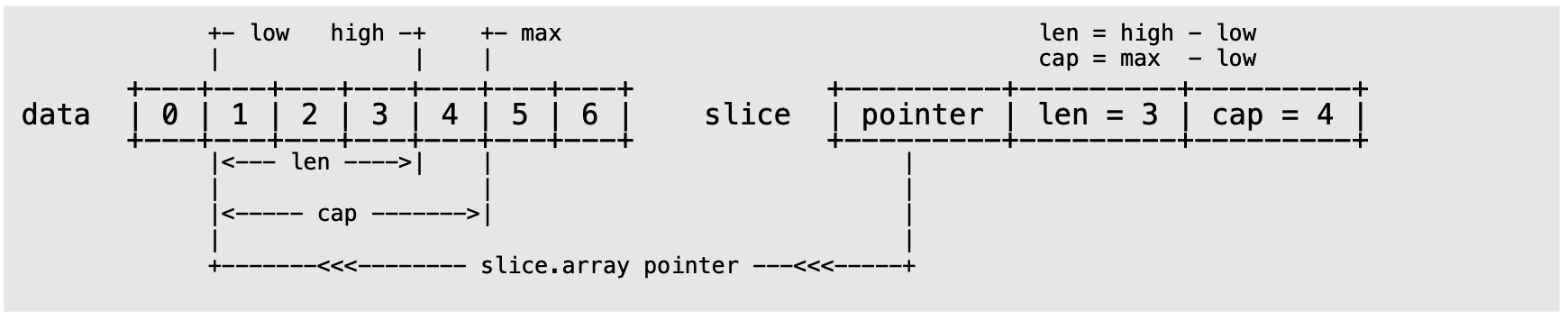 ◎ go slice 结构示意(图片来源于互联网)
◎ go slice 结构示意(图片来源于互联网)
-
append 向 slice 尾部添加数据,超出cap会重新分配底层数组,即使底层数组尚未被填满。
-
通常以2倍容量重新分配底层数组。在大批量添加数据时,建议一次性创建足够长的slice。
-
及时释放不再使用的slice对象。
-
用 copy 函数在两个slice之间复制,复制长度以小的为准。
引用类型,哈希表。
key必须是支持相等运算符的类型。- 迭代时是乱序的,但是能保证所有键值都被迭代完成。
- 可以在迭代时安全的删除键值,但是有新增操作则结果不可预知。
- 获取一个不存在的键值,当键不存在时返回值类型的零值。
slice 取不存在的下标索引会下标越界错误。
- 判断一个键
k是否存在:
1
2
3
|
var x = make(map[int]int, 2)
val, ok := x[1]
fmt.Println(val, ok)
|
输出:0 false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func main() {
var mp = map[string]string{
"c": "c",
"a": "a",
"y": "y",
"x": "x",
}
var keys []string
for k := range mp {
keys = append(keys, k)
}
sort.Strings(keys)
for _, v := range keys {
fmt.Printf("key:%s value:%s\n", v, mp[v])
}
}
|
输出:
1
2
3
4
|
key:a value:a
key:c value:c
key:x value:x
key:y value:y
|
将map的值存储到键值对结构体的切片中,再使用 sort 接口实现排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
func main() {
var mp = map[string]string{
"c": "c",
"a": "a",
"y": "y",
"x": "x",
}
var pl PairList
for k, v := range mp {
pl = append(pl, Pair{k, v})
}
sort.Stable(pl)
for _, v := range pl {
fmt.Printf("key:%s value:%s\n", v.Key, v.Val)
}
}
// Pair 键值对存储到结构体中
type Pair struct {
Key string
Val string
}
// PairList 键值对切片类型
type PairList []Pair
func (p PairList) Swap(i, j int) { p[i], p[j] = p[j], p[i] }
func (p PairList) Len() int { return len(p) }
func (p PairList) Less(i, j int) bool {
a := strings.Compare(p[i].Val, p[j].Val)
return a < 0
}
|
输出:
1
2
3
4
|
key:a value:a
key:c value:c
key:x value:x
key:y value:y
|
除了以上所述对原生map的排序,还可以利用container/list实现可以有序迭代的"map"。
以下直接贴出来自《实现有序map之go》的实现方式。备后续查用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
type Keyer interface {
GetKey() string
}
type MapList struct {
dataMap map[string]*list.Element
dataList *list.List
}
func NewMapList() *MapList {
return &MapList{
dataMap: make(map[string]*list.Element),
dataList: list.New(),
}
}
func (mapList *MapList) Exists(data Keyer) bool {
_, exists := mapList.dataMap[string(data.GetKey())]
return exists
}
func (mapList *MapList) Push(data Keyer) bool {
if mapList.Exists(data) {
return false
}
elem := mapList.dataList.PushBack(data)
mapList.dataMap[data.GetKey()] = elem
return true
}
func (mapList *MapList) Remove(data Keyer) {
if !mapList.Exists(data) {
return
}
mapList.dataList.Remove(mapList.dataMap[data.GetKey()])
delete(mapList.dataMap, data.GetKey())
}
func (mapList *MapList) Size() int {
return mapList.dataList.Len()
}
func (mapList *MapList) Walk(cb func(data Keyer)) {
for elem := mapList.dataList.Front(); elem != nil; elem = elem.Next() {
cb(elem.Value.(Keyer))
}
}
type Elements struct {
value string
}
func (e Elements) GetKey() string {
return e.value
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("Starting test...")
ml := NewMapList()
var a, b, c Keyer
a = &Elements{"Alice"}
b = &Elements{"Bob"}
c = &Elements{"Conrad"}
ml.Push(a)
ml.Push(b)
ml.Push(c)
cb := func(data Keyer) {
fmt.Println(ml.dataMap[data.GetKey()].Value.(*Elements).value)
}
fmt.Println("Print elements in the order of pushing:")
ml.Walk(cb)
fmt.Printf("Size of MapList: %d \n", ml.Size())
ml.Remove(b)
fmt.Println("After removing b:")
ml.Walk(cb)
fmt.Printf("Size of MapList: %d \n", ml.Size())
}
|
 ◎ go slice 结构示意(图片来源于互联网)
◎ go slice 结构示意(图片来源于互联网)