其实这个没有什么讲的,同样网上一搜一大把,就简单的说一下吧。
- nsqd 在整个nsq体系中这个充当生产者角色,可以独立运行。pub,sub,mpub等等一系列操作都是通过这个服务实现的,在整个服务体系中作为一个节点。一般建议和产生消息的业务程序部署在同一个机器。
- nsqlookup 是一个服务发现程序,虽然nsqd可以独立运行但是nsq本身是一个分布式消息队列系统,nsqlookup可以为服务的发现提供支持。配置好后在nsqd中会注册到一个nsqlookup服务,nsqlookup会定时发送心跳检查指令测试nsqd的状态。消息消费程序可以通过nsqlookup获取可用的nsqd服务并执行订阅、消息发布等一系列操作。
- nsqadmin是一个提供web界面的nsq管理服务,在这里可以查看各个服务的运行状态,包括nsqd服务数目以及详情:话题数、每个话题的频道数。频道只有有消费订阅程序连接的时候才是可见并且可点击的。通过查看频道详情你可以知道连接的消费客户端的详细信息,如下图:
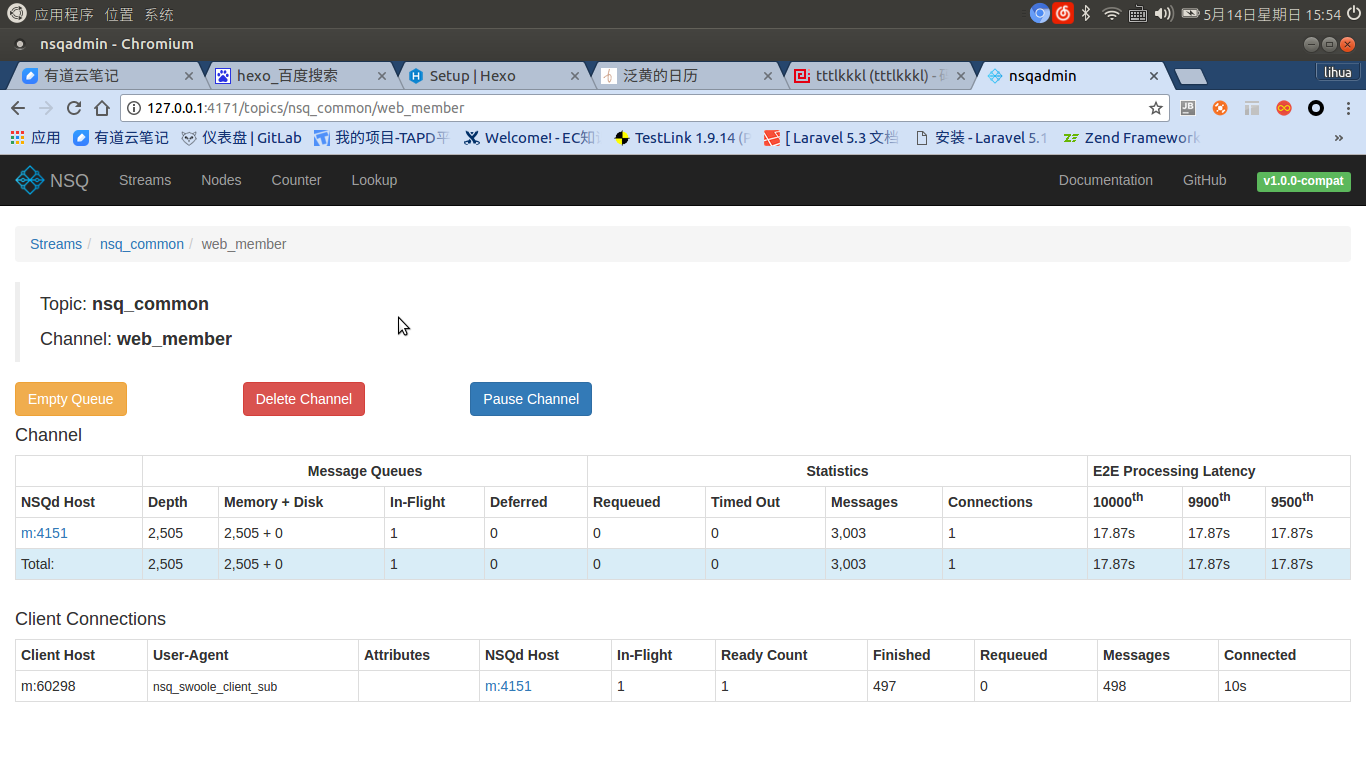
- Client Connections中可以看到客户端的连接信息:
- Client Host :客户端地址。
- User-Agent:客户端自述信息,由客户端定义。
- NSQd Host:nsqd服务地址。
- Ready Count:客户端可读取的消息数目,由客户端决定。客户端中通过“RDY”指令设置。设置1表示将有1条消息被发送到客户端。
- Finished:已消费完毕的消息数,值被发送到客户端并且客户端通过“FIN”指令确认的消息数目。
- Requeued:重新排队的消息数目,标识客户端通过“REQ”指令重新排队的消息数目。
- Messages:当前频道中的消息数目。
- Connected:客户端连接时间。
- nsq工具集,这里就不再扯蛋了。
根据文档说明里的“QUICK START”我们可以快速演示和体验nsq的使用,但是即使用于开发每次都要打开3个终端然后逐个执行启动实在不爽至极。所以将配置都放到文件中,这样也有利于更有利于进行进一步复杂的配置和管理。关于配置文件着一块网上相关资料少之又少,在nsq源码中有几个示例配置,这里拿来简要说一下。
nsq配置文件遵循TOML文件规范,文件后缀名为“.cfg”。为了后续说明这里假设所有配置文件都在/etc/nsq/目录下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
|
##是否启用详细记录
verbose = false
## unique identifier (int) for this worker (will default to a hash of hostname)
# id = 5150
## <addr>:<port>客户端TCP地址,客户端通过这个地址连接nsqd并进行订阅,发布。注意订阅必须通过TCP连接实现。
tcp_address = "127.0.0.1:4150"
## <addr>:<port> 用来进行发布的http端口,经过测试这里的ip只能是nsqd所在机器网卡的任意一个ip,如果填写127.0.0.1只接受本机请求。
http_address = "0.0.0.0:4151"
## <addr>:<port> 用于发布的https端口
# https_address = "0.0.0.0:4152"
## address that will be registered with lookupd (defaults to the OS hostname)
# broadcast_address = ""
## cluster of nsqlookupd TCP 地址,可以设置多个。
nsqlookupd_tcp_addresses = [
"127.0.0.1:4160"
]
## duration to wait before HTTP client connection timeout
http_client_connect_timeout = "2s"
## duration to wait before HTTP client request timeout
http_client_request_timeout = "5s"
## path to store disk-backed messages
# data_path = "/var/lib/nsq"
## number of messages to keep in memory (per topic/channel)
mem_queue_size = 10000
## number of bytes per diskqueue file before rolling
max_bytes_per_file = 104857600
## number of messages per diskqueue fsync
sync_every = 2500
## duration of time per diskqueue fsync (time.Duration)
sync_timeout = "2s"
## duration to wait before auto-requeing a message
msg_timeout = "60s"
## maximum duration before a message will timeout
max_msg_timeout = "15m"
## maximum size of a single message in bytes
max_msg_size = 1024768
## maximum requeuing timeout for a message
max_req_timeout = "1h"
## maximum size of a single command body
max_body_size = 5123840
## maximum client configurable duration of time between client heartbeats
max_heartbeat_interval = "60s"
## maximum RDY count for a client
max_rdy_count = 2500
## maximum client configurable size (in bytes) for a client output buffer
max_output_buffer_size = 65536
## maximum client configurable duration of time between flushing to a client (time.Duration)
max_output_buffer_timeout = "1s"
## UDP <addr>:<port> of a statsd daemon for pushing stats
# statsd_address = "127.0.0.1:8125"
## prefix used for keys sent to statsd (%s for host replacement)
statsd_prefix = "nsq.%s"
## duration between pushing to statsd (time.Duration)
statsd_interval = "60s"
## toggle sending memory and GC stats to statsd
statsd_mem_stats = true
## message processing time percentiles to keep track of (float)
e2e_processing_latency_percentiles = [
100.0,
99.0,
95.0
]
## calculate end to end latency quantiles for this duration of time (time.Duration)
e2e_processing_latency_window_time = "10m"
## path to certificate file
tls_cert = ""
## path to private key file
tls_key = ""
## set policy on client certificate (require - client must provide certificate,
## require-verify - client must provide verifiable signed certificate)
# tls_client_auth_policy = "require-verify"
## set custom root Certificate Authority
# tls_root_ca_file = ""
## require client TLS upgrades
tls_required = false
## minimum TLS version ("ssl3.0", "tls1.0," "tls1.1", "tls1.2")
tls_min_version = ""
## enable deflate feature negotiation (client compression)
deflate = true
## max deflate compression level a client can negotiate (> values == > nsqd CPU usage)
max_deflate_level = 6
## enable snappy feature negotiation (client compression)
snappy = true
data-path="/www/data/nsq/"
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
## 在浏览器中访问这个地址进入管理。
http_address = "0.0.0.0:4171"
## graphite HTTP address
graphite_url = ""
## proxy HTTP requests to graphite
proxy_graphite = false
## prefix used for keys sent to statsd (%s for host replacement, must match nsqd)
statsd_prefix = "nsq.%s"
## format of statsd counter stats
statsd_counter_format = "stats.counters.%s.count"
## format of statsd gauge stats
statsd_gauge_format = "stats.gauges.%s"
## time interval nsqd is configured to push to statsd (must match nsqd)
statsd_interval = "60s"
## HTTP endpoint (fully qualified) to which POST notifications of admin actions will be sent
notification_http_endpoint = ""
## nsq发现服务地址
nsqlookupd_http_addresses = [
"127.0.0.1:4161"
]
## nsqd HTTP addresses (optional)
#nsqd_http_addresses = [
#"127.0.0.1:4151"
#]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
##enable verbose logging
verbose = false
## <addr>:<port> nsqd通过这个tcp地址注册到nsqlookup
tcp_address = "127.0.0.1:4160"
## <addr>:<port> 消费客户端通过这个地址获取可用的服务列表
http_address = "127.0.0.1:4161"
## address that will be registered with lookupd (defaults to the OS hostname)
# broadcast_address = ""
## duration of time a producer will remain in the active list since its last ping
inactive_producer_timeout = "300s"
## duration of time a producer will remain tombstoned if registration remains
tombstone_lifetime = "45s"
|
根据以上配置将以上文件内容保存到文件中,并通过nsq组件的“-config”指令选项指配置文件可以简化nsq启动过程。如/user/local/nsq/bin/nsqd --config /etc/nsq/nsq.cfg。当然,不论是开发还是生产这还不是最方便有效的方式。利用supervisor管理nsq进程方可一劳永逸。
